Did you know that your gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome? These tiny inhabitants play a crucial role in your overall health, influencing everything from digestion to immune function. In recent years, there has been growing interest in harnessing the power of the gut microbiome for therapeutic interventions. Researchers and scientists are exploring innovative ways to target and manipulate these microorganisms to potentially treat a wide range of diseases and improve human health. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of the gut microbiome and the exciting possibilities it holds for future therapeutic interventions.
Introduction to the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome refers to the collection of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, that reside in our gastrointestinal tract. It is estimated that the gut microbiome contains trillions of microbial cells, collectively known as the gut microbiota. This complex ecosystem plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being.
Definition of the Gut Microbiome
The term “gut microbiome” encompasses the genetic material of these microorganisms and their interactions with the host organism, which is us. It is a dynamic and diverse community that varies from person to person. the composition of the gut microbiome is influenced by various factors, including diet, lifestyle, genetics, and environmental exposures.
Importance of the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome plays a fundamental role in our digestion and metabolism. It helps break down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that our bodies are unable to digest on their own. The gut microbiota also produces essential vitamins, such as vitamin K and certain B vitamins, which are indispensable for our overall health.
Furthermore, the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in our immune system. It helps educate and train our immune cells, ensuring an appropriate balance between inflammation and immune tolerance. Additionally, studies have shown that the gut microbiome can influence our mental health, contributing to conditions such as anxiety and depression.
Targeting the Gut Microbiome for Therapeutic Interventions
Explanation of Therapeutic Interventions
Therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating the gut microbiome have gained significant attention in recent years. These interventions focus on restoring a balanced and diverse gut microbiota in order to improve health outcomes.
Advantages of Targeting the Gut Microbiome
Targeting the gut microbiome offers several advantages over traditional therapies. Firstly, the gut microbiome influences various physiological processes, making it a potential target for a wide range of diseases and conditions. Secondly, interventions targeting the gut microbiome can be relatively non-invasive and have fewer side effects compared to some conventional treatments. Lastly, modulating the gut microbiome has the potential to provide long-lasting effects, as changes in the microbiota composition can persist over time.
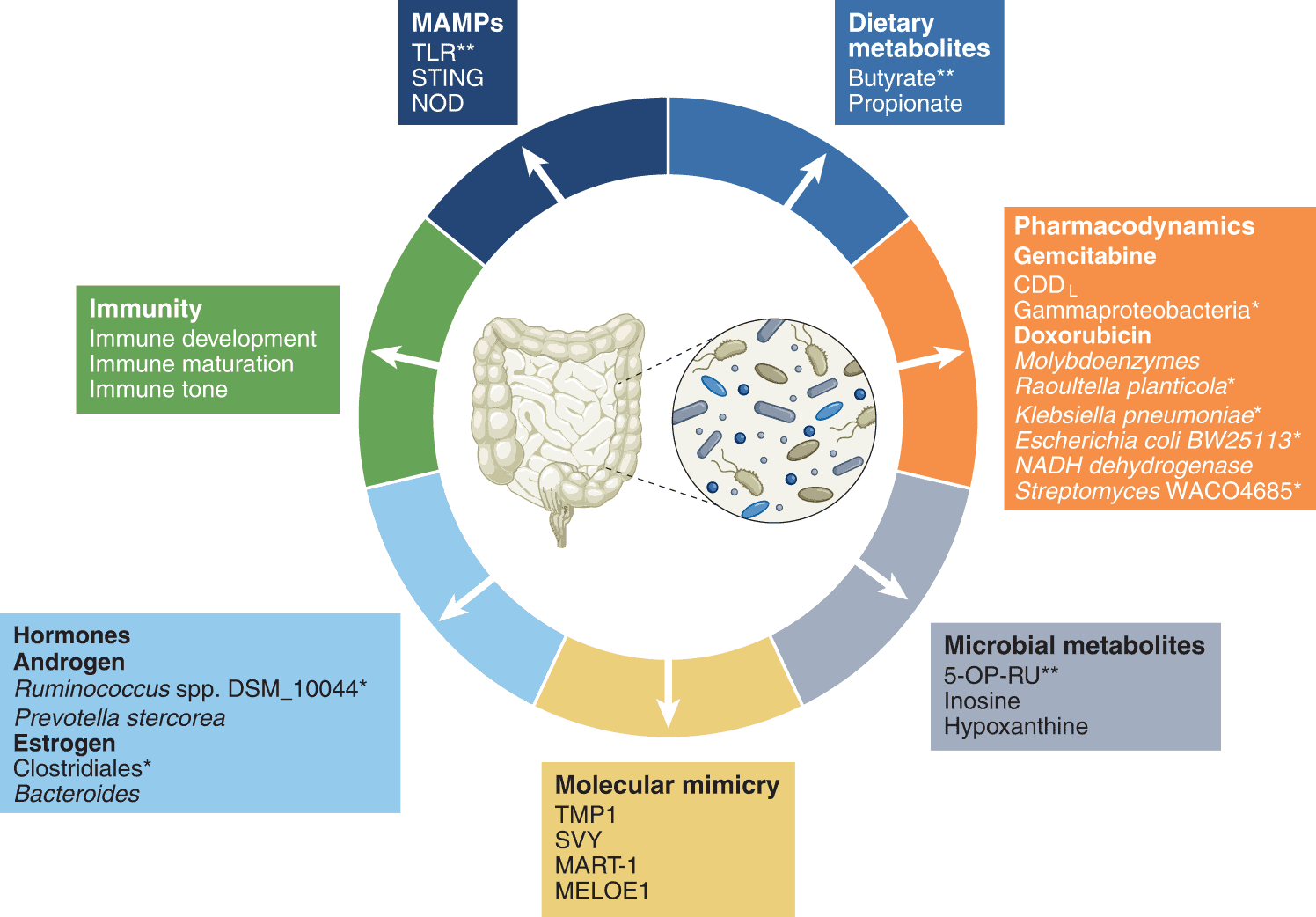
Understanding the Gut Microbiome-Host Relationship
Mutualistic Relationship between Gut Microbiome and Host
The relationship between the gut microbiome and the host can be described as mutualistic, meaning that both parties benefit from this symbiotic association. The gut microbiota aids in the digestion and absorption of nutrients, while the host provides a favorable environment and a steady supply of nutrients for the microorganisms.
Factors Influencing the Gut Microbiome
Several factors can influence the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome. Diet is considered one of the most influential factors, with a plant-based, fiber-rich diet promoting a diverse and healthy microbiota. Other factors, such as genetics, age, medications, and exposure to environmental toxins, can also shape the gut microbiome.
The Role of Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease
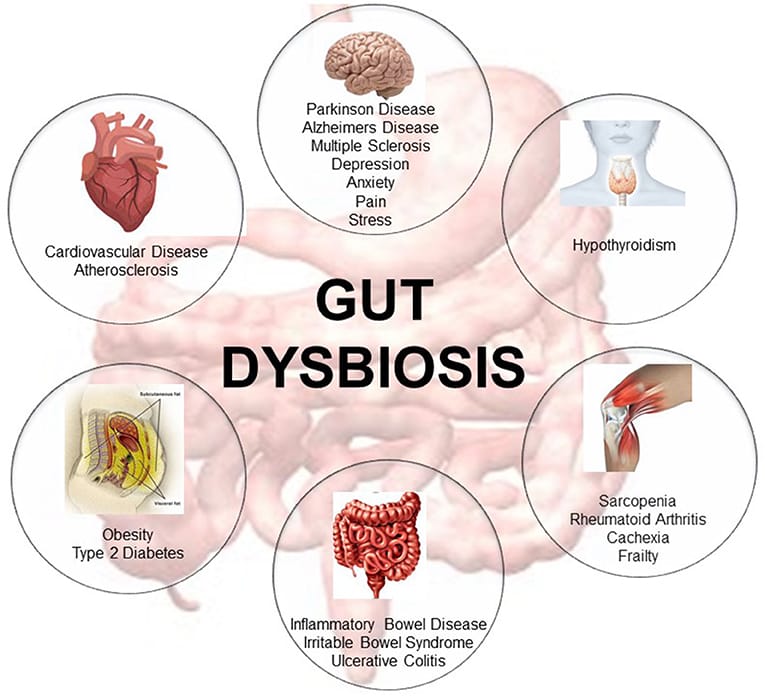
Research has shown that alterations in the gut microbiome are associated with various health conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders, metabolic disorders, autoimmune diseases, and even mental health disorders. Imbalances or dysbiosis in the gut microbiota can disrupt normal physiological functions and contribute to the development and progression of these diseases.
Methods for Modulating the Gut Microbiome
Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
One of the most effective ways to modulate the gut microbiome is through diet and lifestyle modifications. consuming a diverse array of plant-based foods, rich in fiber, can promote a healthy and diverse gut microbiota. Regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep also play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome.
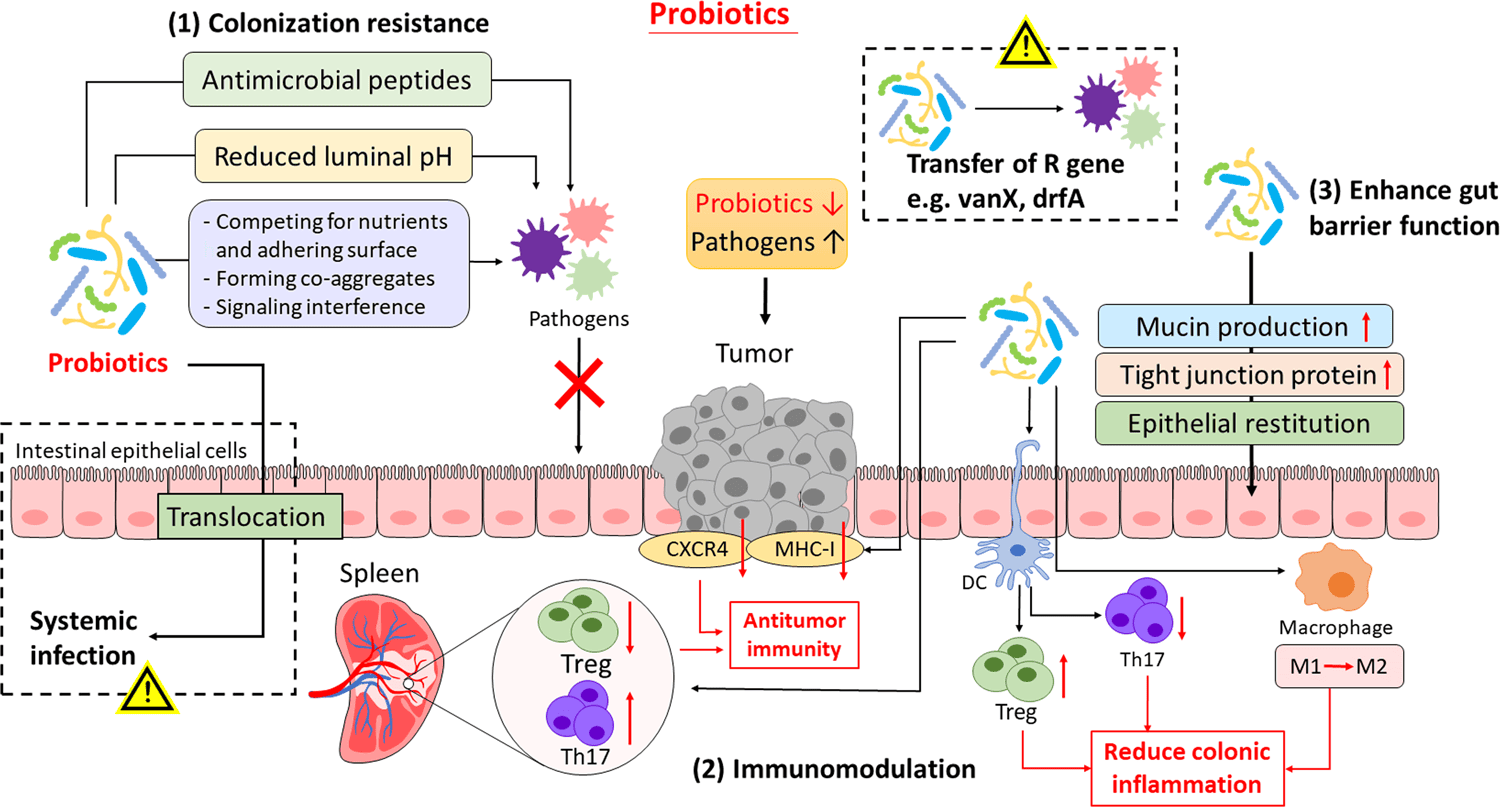
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are living microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits to the host. These beneficial bacteria can be found in certain fermented foods and dietary supplements. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for the beneficial bacteria in the gut. Consuming prebiotics can help promote the growth and activity of these beneficial microbes.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is a procedure in which fecal matter from a healthy donor is transplanted into the gastrointestinal tract of a recipient. This procedure aims to restore a healthy gut microbiota in individuals with severe dysbiosis or recurrent infections. FMT has shown promising results in the treatment of certain gastrointestinal disorders, such as Clostridium difficile infection.
Antibiotics and Other Medications
Antibiotics, while effective in treating bacterial infections, can also have a detrimental impact on the gut microbiome. They can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiota, leading to dysbiosis and potentially causing antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Other medications, such as proton pump inhibitors and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also affect the gut microbiome.

Potential Therapeutic Applications of Targeting the Gut Microbiome
Treatment of Gut-related Disorders
Modulating the gut microbiome shows promise in the treatment of various gastrointestinal disorders, such as inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and gastrointestinal infections. By restoring a healthy balance of the gut microbiota, symptoms can be alleviated and disease progression can be slowed.
Management of Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic disorders, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, have been linked to alterations in the gut microbiome. Therapeutic interventions targeting the gut microbiome, such as diet modifications and probiotic supplementation, have shown potential in improving metabolic health outcomes.
Immune System Modulation
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in educating and modulating our immune system. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota has been implicated in the development of autoimmune diseases, allergies, and other immune-related disorders. By restoring a healthy gut microbiota composition, it may be possible to modulate the immune system and prevent or manage these conditions.
Mental Health and Neurological Disorders
Emerging evidence suggests a link between the gut microbiome and mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and autism spectrum disorders. The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication pathway between the gut and the brain, is thought to play a crucial role in this relationship. Targeting the gut microbiome may offer new avenues for the treatment and management of these conditions.
Challenges in Targeting the Gut Microbiome
Complexity of the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome is an incredibly complex and diverse community, comprising thousands of different species. Understanding the interplay between these microorganisms and their impact on human health is a daunting task. The vast variability between individuals and the dynamic nature of the gut microbiome pose significant challenges in developing targeted therapeutic interventions.
Effectiveness and Long-term Safety
While the potential therapeutic applications of targeting the gut microbiome are promising, the effectiveness and long-term safety of these interventions require further investigation. More research is needed to determine the optimal strategies for modulating the gut microbiome and to assess the potential risks and benefits associated with these interventions.
Ethical Considerations
The use of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) raises ethical considerations, particularly with regard to donor screening and consent. Ensuring the safety and efficacy of FMT procedures is of utmost importance to protect both donors and recipients. Additionally, the potential for commercialization of gut microbiome-targeting interventions raises questions about accessibility, affordability, and equity in healthcare.
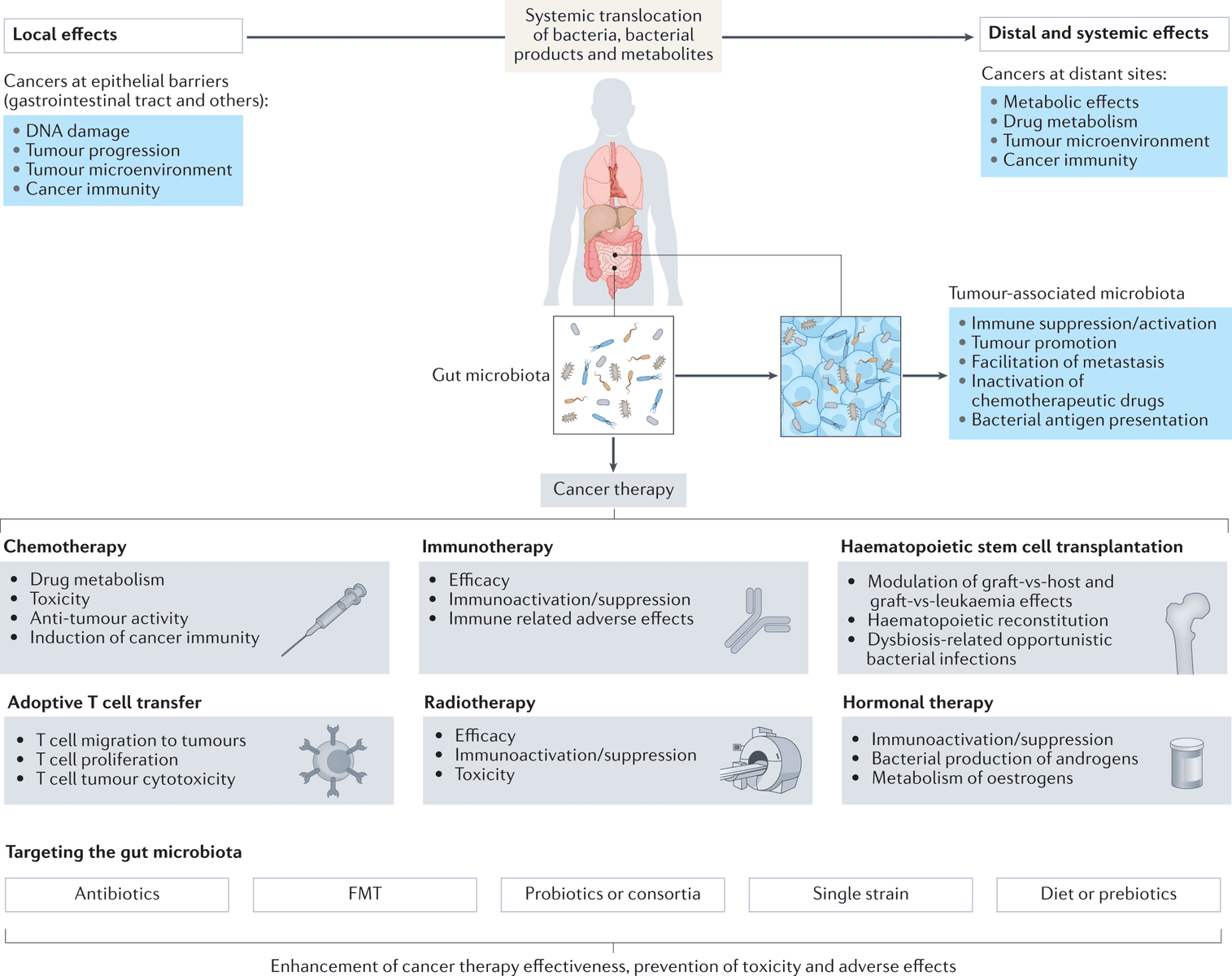
Future Perspectives and Research Directions
Advancements in Gut Microbiome Research
The field of gut microbiome research is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and methodologies continually advancing our understanding. Advances in sequencing technologies, artificial intelligence, and metabolomics hold promise for unraveling the complexities of the gut microbiome and its interactions with the host.
Personalized Medicine and Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome is highly individualized, and its composition is influenced by various factors, including genetics. Personalized medicine approaches that take into account an individual’s specific gut microbiota profile hold tremendous potential for tailoring treatments and interventions to optimize outcomes.
Potential for Drug Development
The gut microbiome has been identified as a potential target for the development of novel therapeutic agents. Researchers are exploring the use of microbiome-targeted drugs, such as bacteriophages and small molecules, to selectively modulate the gut microbiota and treat various diseases.
Conclusion
The gut microbiome is a fascinating and complex ecosystem that plays a crucial role in our health and well-being. Targeting the gut microbiome for therapeutic interventions holds tremendous potential for improving outcomes in a wide range of diseases and conditions. However, several challenges need to be addressed, including the complexity of the gut microbiome, the effectiveness and safety of interventions, and ethical considerations. Continued research and advancements in the field of gut microbiome research will undoubtedly shed more light on this intricate relationship and open new doors for personalized medicine and innovative drug development.